Examples of unit conversion and related checks in internal data transfer Top unit 9020 9021 9022 9023 9024 9030 9031 9032 9033 9033a 9033b Table 20: Data type connections and user rights
User needs 'read' rights to the source units if source data is not deleted, or 'write' rights if data is deleted. User needs 'write' rights to target units. Internal data transfer options •Unit: 9030 •Source data type: ACT •Target data type: BUD Units retrieved from the source data: 9031, 9032, 9033a, 9033b Table 21: Example 1
No conversion table is needed in this case. When the sub-units are not input units in the target structure, data is transferred automatically from the sub-units to the parent unit. Transfer execution: •User 1: Transfer succeeds. •User 2: Transfer fails, because the user does not have rights to all source units (9033a, 9033b). Table 22: Example 2: Unit conversion table
Table 23: Conversion table expanded to show the mapping of source units to target units in input level
Table 24: Conversion rows for the transfer
Transfer execution: •User 1: Transfer succeeds. Units 9031 and 9032 are not input units in the target and their data is transferred to parent unit 9030. •User 2: Transfer fails because user does not have rights to units 9033a and 9033b. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
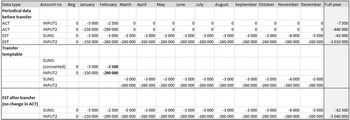
Example: The actual amounts of a month are copied to the estimate data type. The estimate is then updated manually. Table 25: Example 1: Transferring periodical amounts Internal data transfer options
Table 26: AccConvTable2 conversion table
Table 27: Relevant account properties
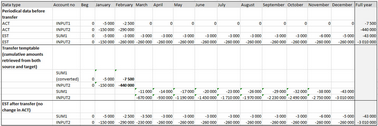
Transfer run result: Figure 102: Transfer run result The full year estimate changes due to a difference in the previous estimate and actual for February. Table 28: Example 2: Transferring cumulative amounts Internal data transfer options
Table 29: AccConvTable2 conversion table
Table 30: Relevant account properties
Transfer run result: Figure 103: Transfer run result The full year estimate does not change. March periodical estimate is adjusted due to a difference in the February actual compared to the previous estimate. |
Example 1 Data type EST has an account used for manual estimates that is not connected to data type ACT. In ACT, this information is recorded on a more detailed level to several accounts. Table 31: Replacing target data
•If Replace target data is not selected, the data in the target account 100 remains because the account is not connected to ACT. •If Replace target data is selected, the data in the target account 100 is deleted. Example 2 When Replace target data is selected, data is replaced for all selected accounts/units that exist in the target structure, including sub-accounts/units that do not exist in the selected source structure. Table 32: Replace target data conversion table
Table 33: Result in BUD after transfer when Replace target data selected
•Data is replaced (deleted) from units 103, 104, and 105, which are sub-units of 100 and are not connected to the source data type. •The data of unit 201 is replaced with data from the source unit 101 based on the conversion table. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||